Team Botanik: Sprint 1 Prototype
Online Abuse and Harrasment Preliminary Research
How does Twitter work?
Twitter is a social network platform that uses micro-blogging for communication. Users can share short messages and media with their followers and the rest of the world.
How It Works

Join or start any conversation in the world by posting a Tweet.

Retweet other users' tweets to spread the ideas.

Follow users who are interesting to keep up with their updates.

Use hashtags to contribute to ongoing conversations.
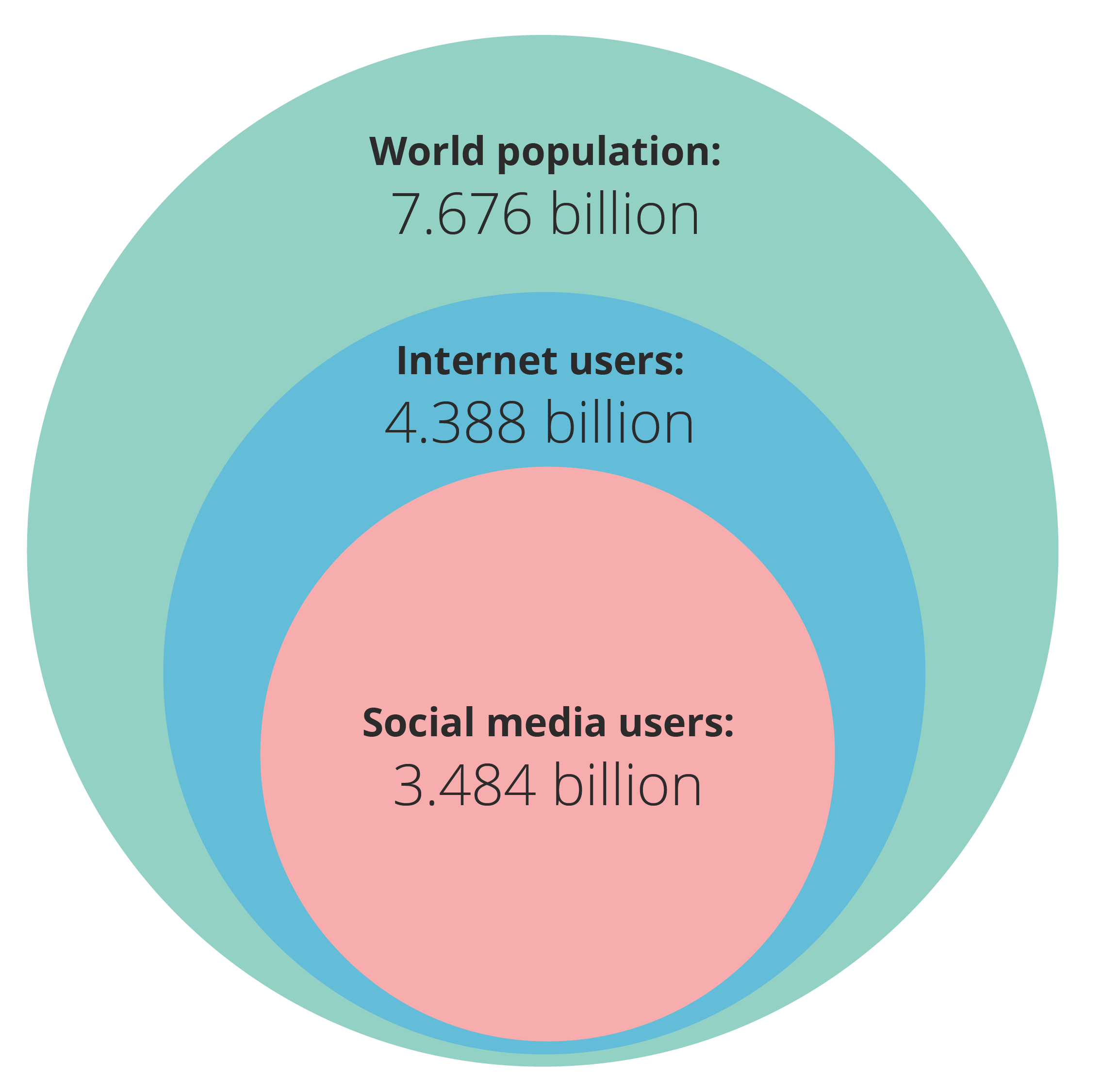
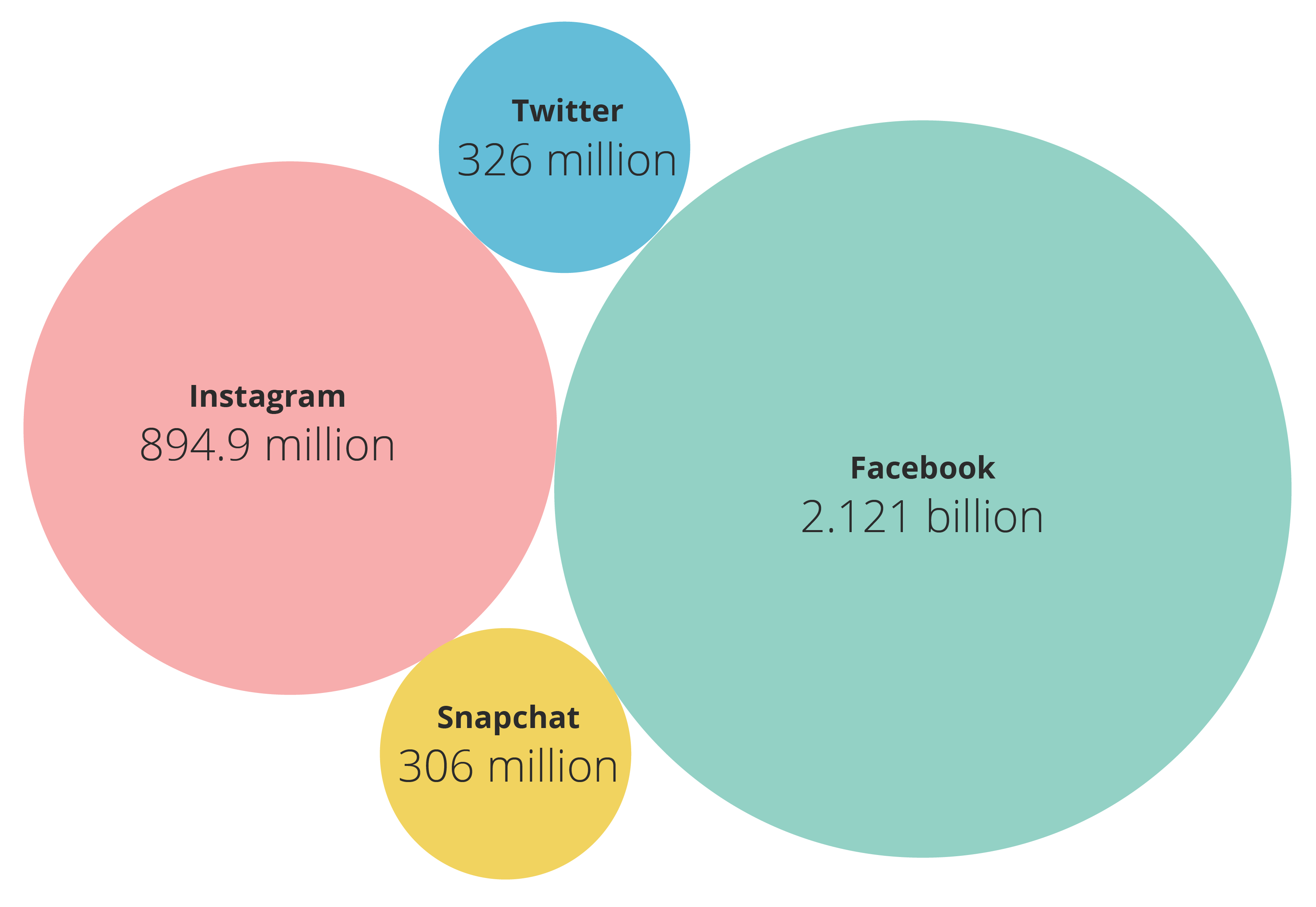
Twitter Statistics

Deinitions of Abuse
Abuse
verb: use (something) to bad effect or for a bad purpose; misuse. Treat with cruelty or violence, especially regularly or repeatedly. To speak to (someone) in an insulting and offensive way.
Abuse is targeted harassment of someone, or incite other people to do so. We consider abusive behavior an attempt to harass, intimidate, or silence someone else’s voice.
Hateful content promotes violence against or directly attack or threaten other people on the basis of race, ethnicity, national origin, sexual orientation, gender, gender identity, religious affiliation, age, disability, or serious disease.
Glossary
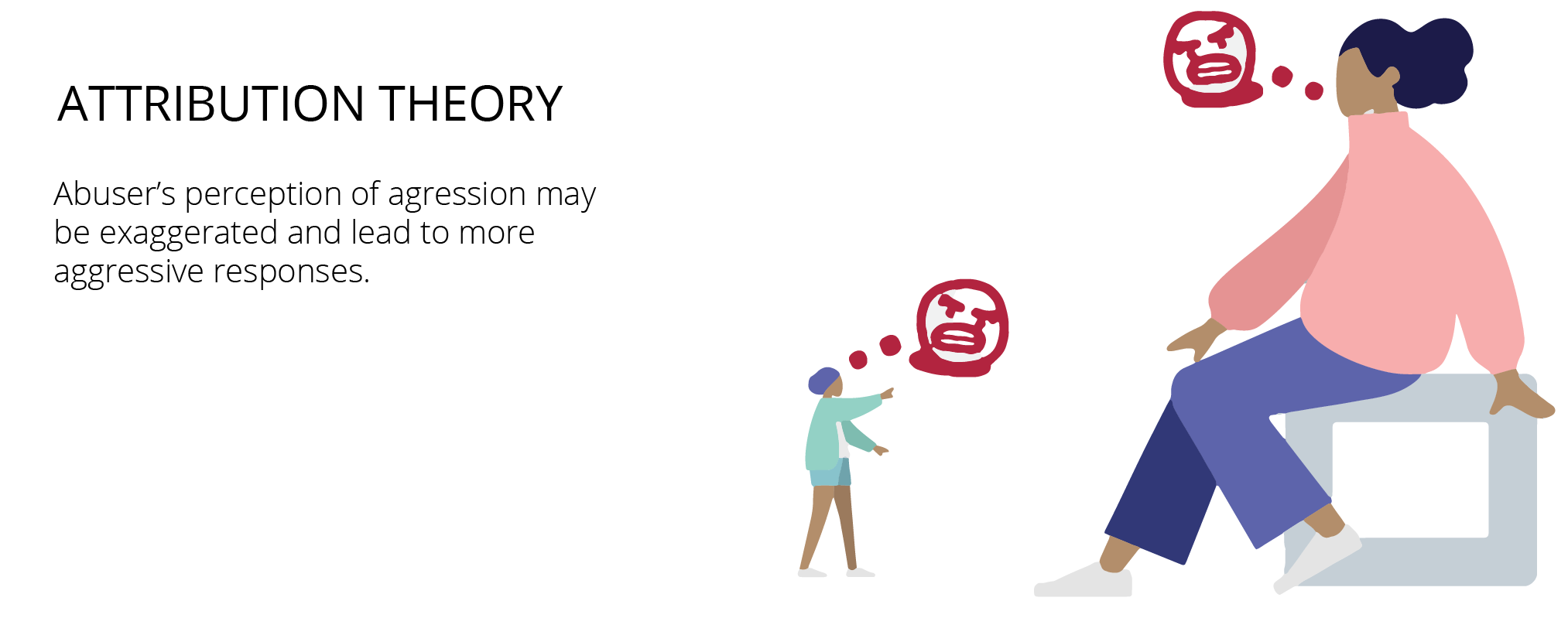
Attribution theory
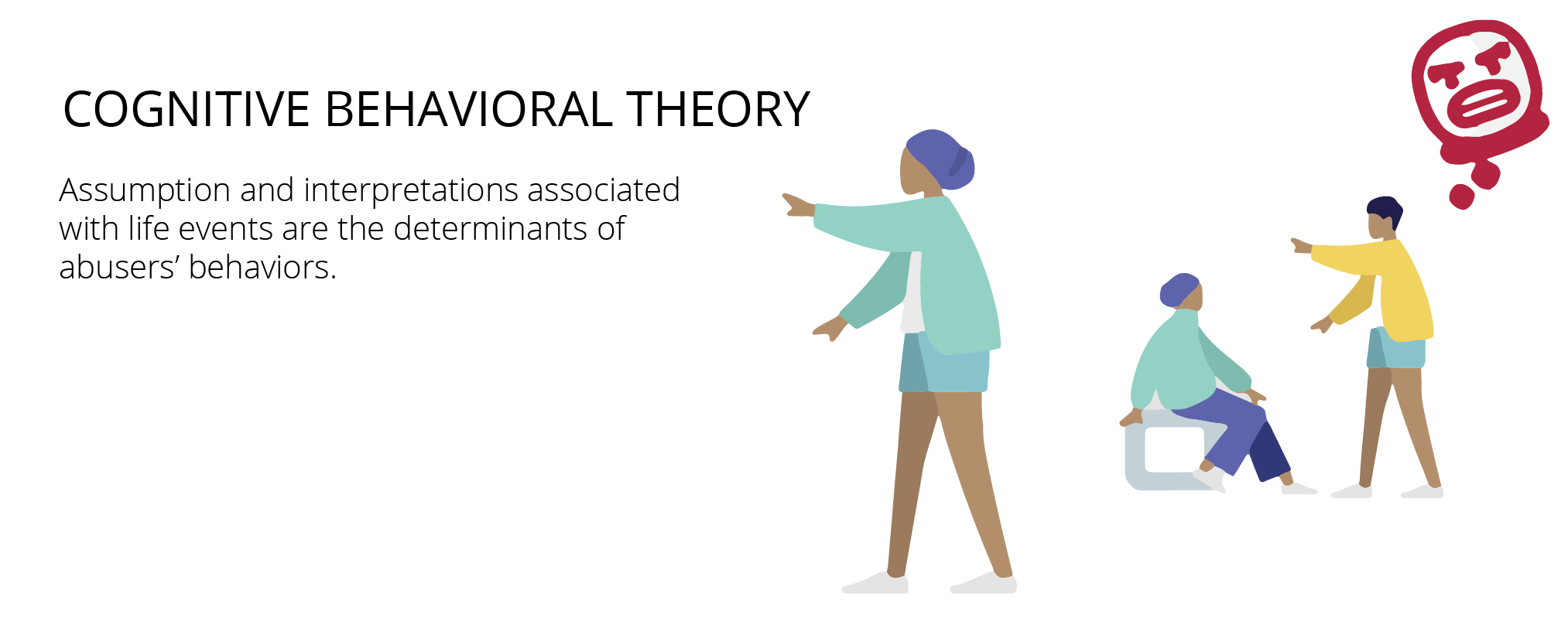
Attribution theory is concerned with how ordinary people explain the causes of behavior and events. For example, is someone angry because they are bad-tempered or because something bad happened?
Source | Back to top
Bot trolling/sockpuppet trolling
Bot accounts come in two flavors: automated accounts, which are controlled by a code or an app in order to impart a particular agenda, and individual accounts, which are set up by a single user with the intention of mimicking real users (known as “sockpuppet” accounts.
Source | Back to top
Brigading
Organising a mass online action to harras one specific person or group of people
Bullying 1. bullying is equated to the concept of harassment, which i.s a form of unprovoked aggression often directed repeatedly toward another individual or group of individuals. 2. Aggressive behavior that is intentional and that involves an imbalance of power. Most often, it is repeated over time. 3. bullying includes the intent to harm, repetition, and a power imbalance between the student targeted and the student who bullies.
Source | Back to top
Coercion theory
Coercion Theory developed by Gerald Patterson and colleagues at the Oregon Social Learning Center (OSLC), describes how aggressive and antisocial behaviors develop in children. Derived from extensive behavioral research on the moment-to-moment interactions in families, it specifies how ineffectual parental responses to problem behavior result in escalating aversive and aggressive behaviors in children in the short-term. It also describes how frequent repetitions of such coercive cycles result in a progressive worsening of aggressive behaviors in both variety and intensity coincident with lack of parental control over the aggression.
Source | Back to top
Concern trolling
hen harassers pose as fans or supporters of your work with the intention of making harmful or demeaning comments masked as constructive feedback. (According to Sarkeesian, “when targeting women, this is most often done through ‘helpful’ suggestions on how to improve one’s appearance. . . . The concern troll’s disingenuous comments are actually designed to undercut or demean you. Source | Back to top
Cyber-Mob Attacks
A cyber-mob attack occurs when a large group gathers online to try to collectively shame, harass, threaten, or discredit a target.
Source | Back to top
Cyberbullying
An umbrella term (like “online harassment”) meant to encompass a number of harassing online behaviors. Like physical bullying, “cyberbulling” is generally aimed at young people and may involve threats, embarrassment, or humiliation in an online setting.
Source | Back to top
Cyberstalking
In a legal context, “cyberstalking” is the prolonged use (a “course of conduct”) of online harassment intended “to kill, injure, harass, intimidate, or place under surveillance with intent to kill, injure, harass, or intimidate” a target.
Source | Back to top
Dogpiling
When a group of trolls works together to overwhelm a target through a barrage of disingenuous questions, threats, slurs, insults, and other tactics meant to shame, silence, discredit, or drive a target offline.
Source | Back to top
Doxing
Doxing, or doxxing, involves publishing someone’s sensitive personal information online in an attempt to harass, intimidate, extort, stalk, or steal the identity of a target. “Sensitive information” can include social security numbers, phone numbers, home addresses, personal photos, employment information, email addresses, and family members’ personal information.
Source | Back to top
Impersonation (or, Impersonation Trolling)
Online impersonation” is a strategy whereby harassers create hoax social media accounts, usually in order to post offensive or inflammatory statements in your name. In most cases, the harasser’s intention is to defame or discredit you, often by convincing others to believe the fake quotes attributed to you, which might then incite others to commit additional acts of harassment. Impersonation trolling can also happen when a harasser impersonates someone you know in order to offend or hurt you.
Source | Back to top
Nonconsensual sharing
Intimate images and videos (such as “revenge porn”). By far the most common form of online harassment, hateful speech or threats, both explicit and implicit, can be issued by an ill-intentioned internet user pretty much anywhere on the web.
Source | Back to top
Online Sexual Harassment
Online impersonation” is a strategy whereby harassers create hoax social media accounts, usually in order to post offensive or inflammatory statements in your name. In most cases, the harasser’s intention is to defame or discredit you, often by convincing others to believe the fake quotes attributed to you, which might then incite others to commit additional acts of harassment. Impersonation trolling can also happen when a harasser impersonates someone you know in order to offend or hurt you.
Source | Back to top
Social Theory
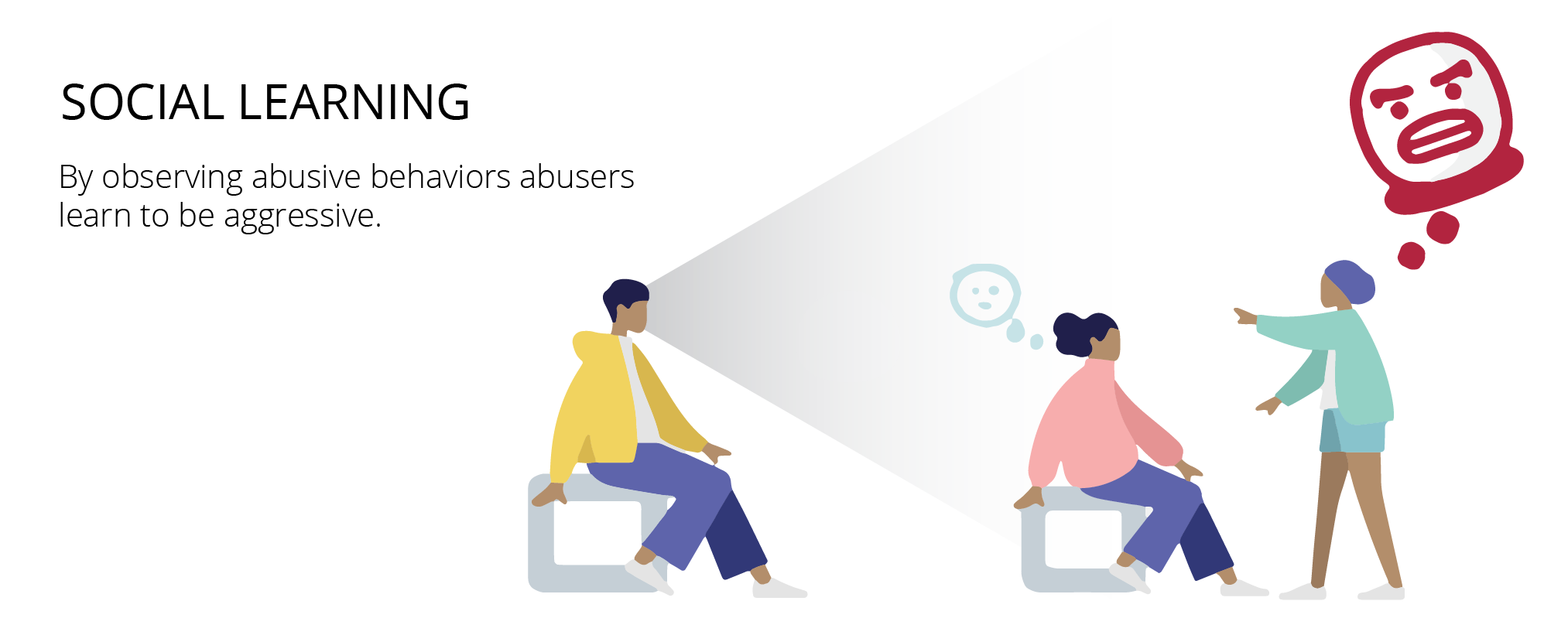
It is a theory of learning process and social behavior which proposes that new behaviors can be acquired by observing and imitating others.
Source | Back to top
Swatting
Swatting doesn’t take place online, but it is often the direct result of online harassment and doxing. It is also one of the most frightening examples of how online harassment can cross dangerously into one’s offline life. Swatting occurs when a hoax call is placed to law enforcement detailing a completely false but plausibly threatening event that the caller claims is taking place in a target’s home or business. | Back to top
Trolling
“Trolling” is one of those terms that’s evolved so much over time as to have no single agreed-upon meaning. Internet users use the word to denote everything from serious acts of online hate speech to the playful distribution of memes and comments on a friend’s social media page.
Source | Back to top
Twitter Abuse Stats
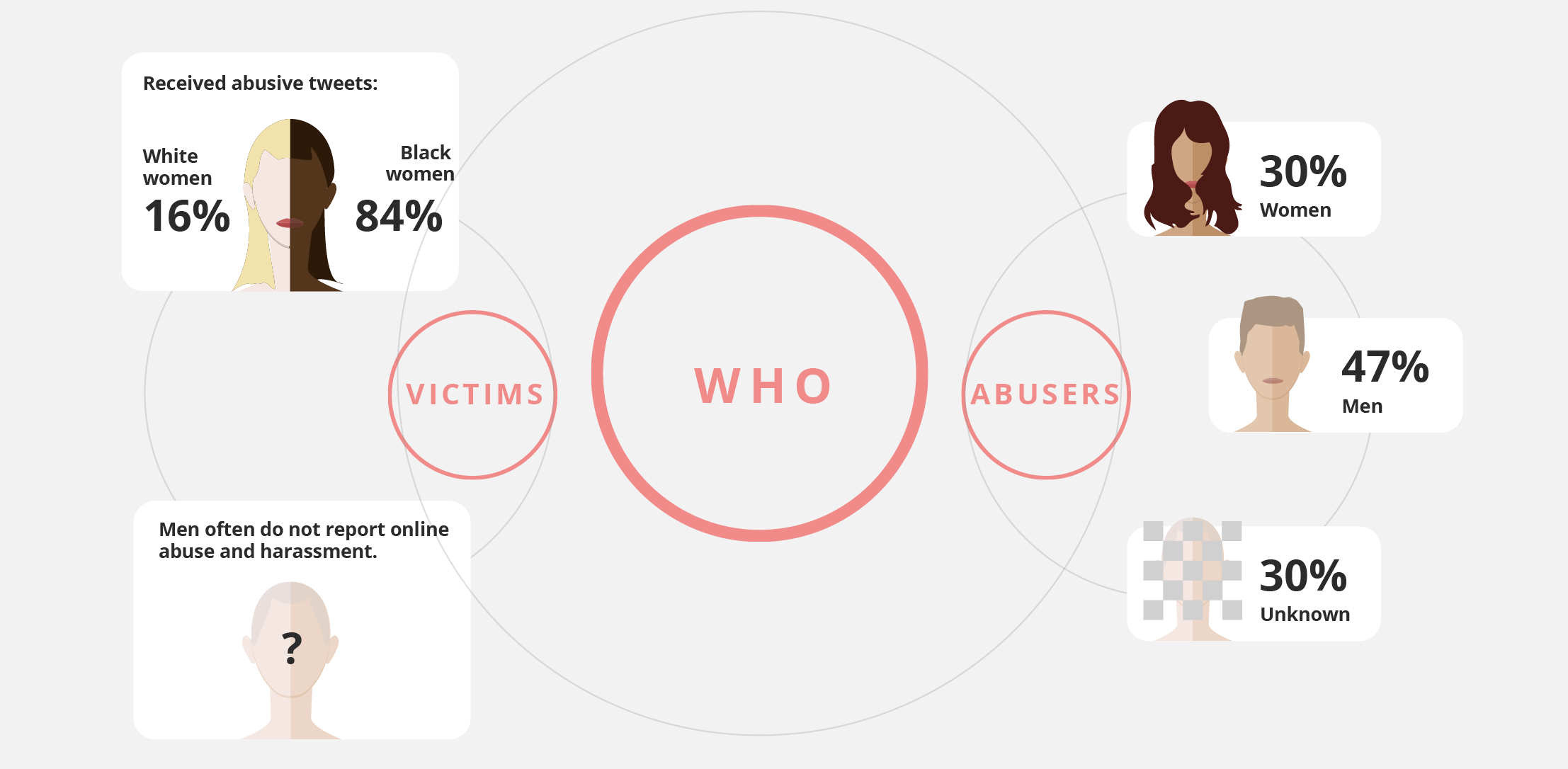
Who are the victims of abuse?
"I’m targeted for being a black woman who works for a black media organization."
AGE: 30 years old
GENDER: Female
OCCUPATION: Journalist
ETHNIC BACKGROUND: Black
POLITICAL AFFILIATION: Left leaning parties
STORY: Part of my work is to share and post my work on Twitter, because a lot of people are using Twitter to get their news. Many times after publishing articles I get inappropriate comments if form of hate speech and online threats, that aren’t relevant to my professional work, but mostly based on my ethnical background.
"I got into a political debate online and the person threatened to find information about me and make it go viral. I called them a troll, then they threatened to physically harm me.""
AGE: 27 years old
GENDER: Male
OCCUPATION: Engineer
ETHNIC BACKGROUND: Unknown
POLITICAL AFFILIATION: Unknown
STORY: Men often do not report online abuse and harassment. There is Social pressure for men to avoid reporting it because being seen as a victim often results in a loss of social standing for men.
Who are abusers?

"I’ve been online pretty long now and use the internet basically for anything. It can be quite helpful but you see a lot of dumb stuff there too, unfortunately."
AGE: Unknown
GENDER: Male
OCCUPATION: Gamer
ETHNIC BACKGROUND: Unknown
POLITICAL AFFILIATION: Unknown
TWITTER ACTIVITY (compared to random user):
More friends and followers
More engaged (time active & liking behaviour)
Longer Twitter membership → better usage of features
TWEET CONTENT:
More negative sentiment
Not angry but less happy

"I had a rough day today but Mondays are always hard, I guess. When I look at the user interfaces of some websites I can really understand their bad ratings, I don’t want to waste my after-work hours on other people’s incompetence."
AGE: Any
GENDER: Any
OCCUPATION: Any
ETHNIC BACKGROUND: Any
POLITICAL AFFILIATION: Any
STORY: I live an average life and I don’t think that I have any specific target groups that trigger my anger. Usually, I stay calm in online conversations but when I’m in a bad mood I get more easily irritated (that happens more often after work and in the beginning of the week). Also, when I follow a heated conversation, I quickly become harsher myself.
INFLUENCES:
Mood
Context of discussion
Stakeholders
Internal
- Twitter company (investors, partners, executives)
- Twitter platform (developers, legal)
- Victims
- Abusers
- Bystanders
- $ users whose bottom line is affected by their activity on Twitter
- Interventionists (this is us!)
External
- Social platforms (incl. competitors)
- Media/Journalists
- Governments
- Society
- Academia
Attribution Theory
Social Learning Theory
Coercion Theory

Cognitive Behavioral Theory
Disinhibition Theory



Chatbots
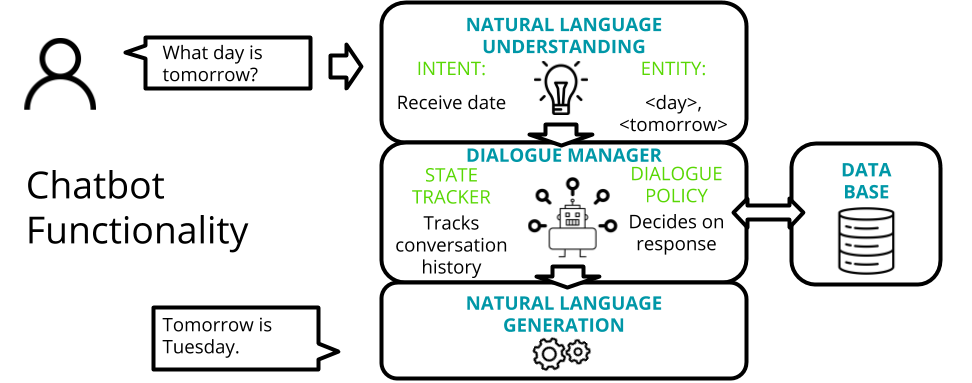

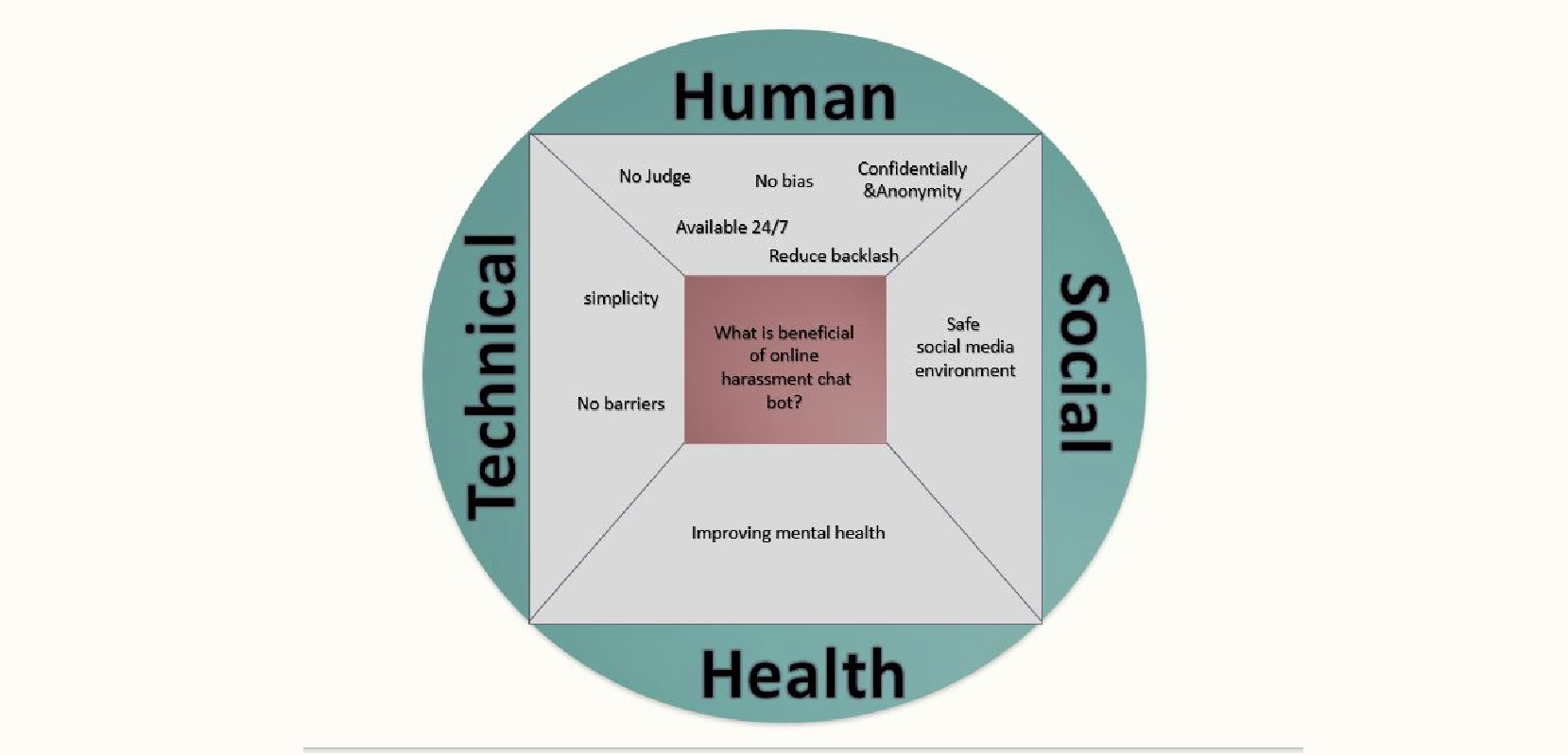

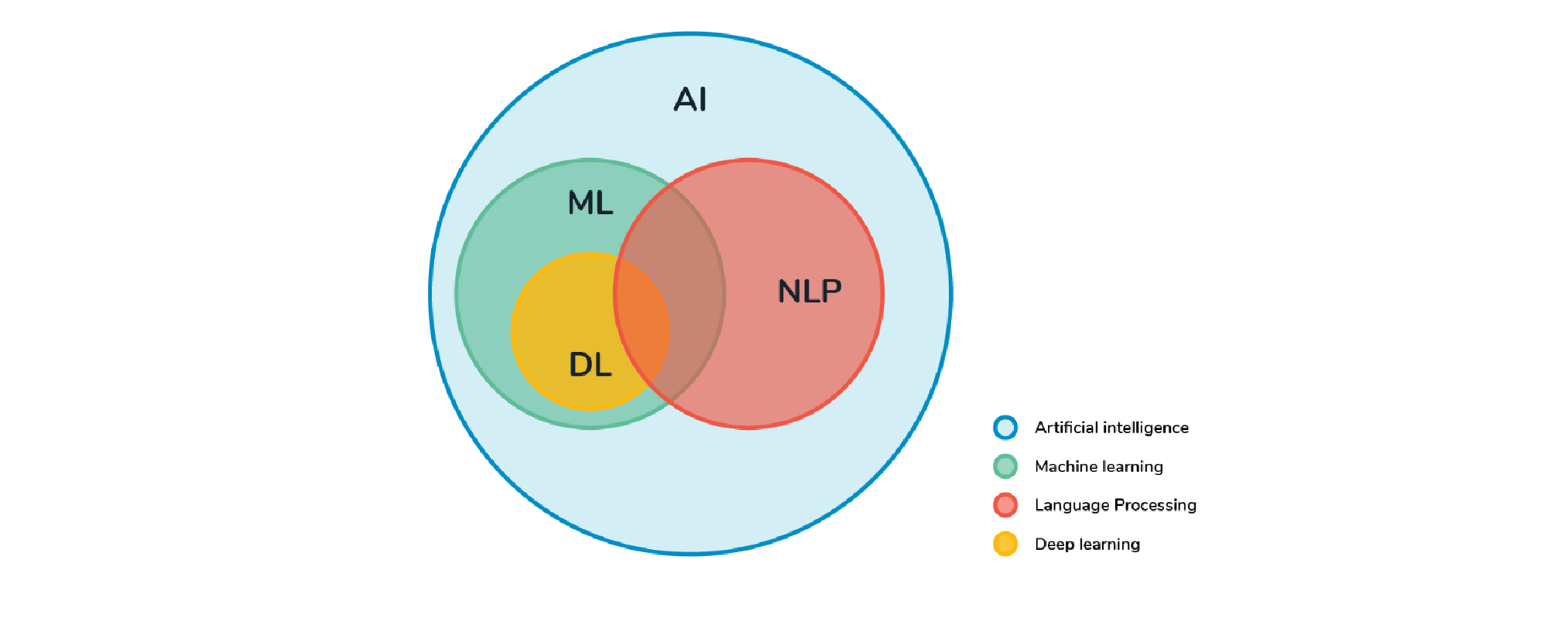
What is AI, ML, NLP?

How to interact with abusers?





What can go wrong?